Well,
failed by 1 questions.
I guess I'll take again in a few months.
Questions were very poorly worded but what can you do.
Monday, March 4, 2013
Saturday, March 2, 2013
Network management
Alright last big chapter.
Network management is done at the last two stages.
Operate, then based on the data accumulated the network will be
optimized...
Statistics will be grabbed on
link utilization - to see if the link needs upgrading
CPU utilization - to see if the device will need upgrading
interface utilization - to see traffic patterns
Cisco Works can centralize configuration changes.
FCAPS is the acronym for this chapter.
Fault management
Configuration management
Accounting Management
Performance management
Security management
This is all done using.
NMS - Network management Systems. This is not a product but a framework for Network management.
In order to run this management the NMS will need.
Network management protocols and standards. - These will be SNMP, RMON,
The NMS will manage devices - these will be the "managed devices"
Inside each device that is being managed there will be a diplomat a "Management Agent".
Snmp Agent
RMON Agent
Netflow can be used instead of RMON.
Syslog can accumulate data from all the devices instead of storing the logs/data locally on each.
SNMP RFC1157
Runs over UDP.
The data in each device is stored in it.
The storage is arranged in a TRee format.
MIB.
The MIB can be queried for the data in the cell/branch by referencing its locations
either by name or number.
Name
Syntax - interger or string
Encoding
Normal Tree would give you basic data like the interface packets.
Cisco has some "private" MIB which will give you the small, med , larg packets.
SNMPv1
Request and Respond mainly.
Get request - let's see get CPU usage - (get response 60%)
Get Request - let's see get route table -(get response 10.0.0.0/24 next-hop 15.15.15.1)
Get Next Request - get response 20.0.0.0/24 next-hop 16.16.16.1)
when the agent responds to the requests he will send a Get response
okay so far we have been reading the fields
Set Request - will enable you to write to a field. set request mib3.3.3.4.5 contactname Saar
pretty useless, I can't find any real implementations of this.
Trap - this is a setting on the agent. When a certain item on the device happens it will try to send an
alert about it to the NMS.
For example on linkdown send to NMS.
SNMPv2
added getbulk that way you don't have to repeat the getnext requests
added inform request basically an improved trap with Confirmation.
SNMPv3
This one finally adds Security.
noAuthnoPriv no authentication at all and no privacy (which means no encryption)
authNoPriv ok, authentication is ok but no privacy. (no encryption)
AuthPriv authentication and Privacy.
Great!!!!
Authentication is MDAC
Encryption is DES, 3DES, AES
RMON
Network Nodes are needed for this.
Can't avoid it.
They are expensive. I think the leader in this is NetScout.
Looks at MAC Layer 2 data.
RMONv1 grabs data from the Layer 1-2
RMONv2 grabs it from the layer 3-7
Netflow is a higher level of the above.
It grabs.
Accounting is the data grabbing
Collectors will grab the data physically.
Analazyers will give you the reporting and GUI for this.
The netflows can be used for billing.
Network planning
Planning for user actions
or Application actions.
CDP
this is a Cisco protocol.
Cisco Discovery Protoocl.
It is helpful for troubleshooting
It runs on Layer 2 level.
syslog allows you to get information from multiple sources.
You can accumulate it all on the Syslog device and then use that to get data.
The levels go from the lowest
Which is the most critical.
0 Emergency
to 6 infomrational
7 debug
Friday, March 1, 2013
Voice and Video
PSTN is circuit switched. Which means that the circuit is built and used for the entire
connection. There is no switching done while the circuit is alive.
CO central office use SS7 in order to route and build the circuit.
The call can be build on Dialup , ISDN , or a TDM.
Each call is 64 kbps of bandwidth and is called a DS0
DS0=64 Kbps.
Old PBXs sit in the enterprise and will give you.
Extension dialing.
VoiceMail
transfers
conferencing
To connect to another site a company can set up a TIE line .
On the TIE line there are no charges to the enterprise.
However the TIE line itself costs money.
Alright, on net which is on the TIE lines.
Off NET to the PSTN.
This will be the same even in VOIP.
If you are using T1's you will call it On-Net
If you are having a call over the internet it will be off-net
PSTN requires you paying charges per each call.
While a Tie line has a fixed monthly cost.
T1 can carry only 24 calls.
24 * 64 = 1280 256 = 1536 Kbps
Now in most books they say T1 is 1.544 Mbps .
So where are the missing 8 bps.
Apparently those are used by the telco for synchronization.
So 23 B channels + 1 D channel = 24 Channel then you need to add 8 Kbps for synchronization.
In the case of Telco. This is ALL used for calls and cannot be used for Data.
Ok.
CO - central office.

This is a map of all the CO (central office) in the USA.
Notice how the west coast has less per mile.
So I drew this up. Since the CCDA one in the book looks pretty useless.
So Tie line is what I buy so I can connect two offices and not pay toll.
Tandem Trunk is what the PSTN provider uses to connect local CO (local exchanges is the correcter term)
Tandem trunks go to a Tandem Switch (class 4)
They will connect to a Class 3 switch which will connect to another Class 3.
Technically if you want to dial abroad then you need to reach a Class 1 switch.
Anyway from Switch 3 to Switch 3 it is and INTER TOLL trunk.
Co to PBX and PBX to Co is just the connection to the CO from the office.
As a note. When you dial in NY. you only need to dial 7 digits since it uses the TANDEM trunks.
When you dial to boston you need the FULL number. it goes on the TOll trunk.
Okay
FXS
Foreign Exchange Service.
We are Exchanging - ie TALKING
In VOIP you will use the same ports to connect OLD equipment to your VOIP network.
Like the ATA from Cisco gives you two FXS ports for the old devices.
So FXS ports
provide Dial tone
Power
Ring Voltage.
Now
FXO is the port that
Ah fuck it.
Just try this.
FXS point to the STATION.
FXO points to the central Office.
So on the phone you have an FXO port
you plug the cable to the FXS port on the PBX
The PBX has an FXO port
that you will plug a cable from the FXO port
to the FXS jack which is the POTS circuit to the Central OFFICE.
E&M ear and mouth - Earth and Magnet.
This is basically a PORT on a PBX. you run an Analog cable which will run to another PORT on PBX2
This allows you to send a signal. This is a TIE trunk for analog.
This has been replaced by BRI PRI digital.
Since we use T1/E1
T1 has 24 channels. It can work either.
CAS Channel associated Signalling - The signalling here is in each channel
In each channel a bit will be robbed for signalling. So 24 channels.
CCS - common channel signalling - This uses one channel for signalling so 23B+D
ISDN uses this and so does SS7
Signalling the state of the phone.
Supervisory signalling tell if it is on hook or off hook
Addressing sends the digits.
Informational sends you the BUSY
Loop start - residential CO to Phone. When you lift the handset the circuit is closed.
Ground Start - CO to phone signals to the switch that it is about to take the line.
helps prevent glaring which is when both take the line at the same time.
E&M - PBX to PBX Two wire - four wire adds more signalling
CAS T1 occurs in band
CSS T1 sets up a separate channel for the signalling
QSig Q.931 used for ISDN between PBX to PBX and Hybrid to CUCM
SS7 inter PSTN switches signalling used by the PhoneProvider.
Loop Start
the CO has the Power 48 DC.
That is why a phone does not need electricity.
When you lift the handset the circuit is closed (off hook) and the power flows all the way to
the phone and back to the CO which sends a dial tone.
Ground Start.
Uses TIP and RING
The PBX has a TIP detector
When the CO grounds the TIP
the PBX detects this and will ground the RING.
Now the CO power 48DC can flow and the arrival of the 48 DC will signal to the CO to send Dial tone.
If the PBX wants to ring.
It will ground the RING which will be detected by the CO.
The CO will ground the TIP
Now the CO power 48 can flow and when it reaches the CO it send Dial tone
E&M
type I and type II are in the USA
type III is everywhere.
Type V is outside the USA.
Immediate start wait 200ms and send
Wink - wait for on hook from other side and then sends.
Delay start - lift wait for 200ms check if on hook. if still off-hook then wait till on-hook.
on hook means
Off- hook means
SS7 signalling
So
Best I can do STP would be internal.
SCP for control - controls 800-900 and credit cards
Sending the Dialing Numbers
Pulse - rotary - sends 5 signals 1 1 1 1 1 = 5
DTMF - sends Two tones at the same time. X+Y = 5
NANP
North American - numbering plan
country-area-office-line
nxx-nxx-xxx-xxxx
Centrex - the CO has the PBX
VoiceMail -
Database or CDR keeps data on the calls. You can get reports.
IVR - interactive for accounting press 5 for Jamil press 2
ACD - used for call centers - how long the calls + statistics.
Grade of service.
P.02 GOS = means 2% of calls won't make it
P.01 GOS - means 1% won't make it and will be blocked.
Earlang B.
You have 24 channels
if one is taken for a whole hour = 1 Earlang.
You measure it at the busy hours.
30 calls * 10 minute per call = 300 minutes 300/60 = 5 Earlangs.
So you run Earlang with the GOS to calculate the number of lines you need.
Earlang B extended
Same thing but takes into account some people will retry to call.
Earlang C
Same thing but instead of blocking calls will put them on HOLD.
Used for C callcenter.
Call second = 1 second of calls.
Centrum = cent 100 seconds
1 Centrum * 36 = 1 Earlng
Busy Hour also called Peak Hour
Busy Hour traffic.
average call duration (20 minutes) * number of calls (6) = 120 minutes/60 = 2 Earlangs.
If you have the length of the calls in seconds.
Then you need to divide it in seconds. So instead of 60 minutes you use 3600 seconds.
So an example.
each call is 300 seconds * 400 calls = 120,000 seconds / 3600 seconds = 33.333 earlangs.
Eventually you will have blocked calls. They are the GOS you plan for.
CDR
call detail records done by the PBX
ACD distributes calls to agents.
Cisco Unified Network
Network is at the base.
Call routing done by the CUCM / SRST dial plans and PST gateway
Call Control on off to the LDAP
Applications and services like chat or voicemail or contact center
Operations and Service Quality
VoFR - over frame relay
VoATM - over ATM
VOIP is now the leader.
Voice over IP.
PSTN is not flexible
Data networks are
You can also save money by adding it all on the DATA network.
SRST - backup goes to PSTN . Overflow of traffic goes to PSTN.
Cisco IPT IP telephony.
Network is the base.
Gateways convert from VOIP to analog
CUCM is the brains of the dial plan and routers VOIP
Single Site - one CUCM at HQ
Multi site CENTRALIZED - CUCM at HQ and SRST at branches
Multi site Distributed - CUCM at each location .
In a multi-site distributed.
Each Cluster up to 30000 users.
To connect clusters use Inter-cluster trunk
GateKeepers will keep them in sync and enforce CAC
CAC is call access control. Which prevents too many calls on the line. So the call quality is kept up.
Call manager express is one appliance that does the mailbox, pstn and voip
Video
Telepresence which is the Cisco Video conferencing is many to many and takes 4-12 Mbps HD
Desktop Video to Video - many to many less demand
cameras to hq - many to few many cameras send data to few(hq)
Streaming Video Few to Many - the VOD to many users.
Access for users
Transport for sending the data
Bridging for converting it.
session provide signalling.
Storage store content
Codecs
G711 8000 samples per second * 8bits per sample 64000 = 64 Kbps = DS0
Analog to Digital
Filter the range you want to record. anything above 4000hz will be dropped
sample the speaking 8000 times per second
Digitize it into 0 1 01 1 01010 1 also called PCM pulse to Code modulation
G711 U for USA 64 Kbps
G711 a for international 64Kbps
G729 8 kbps
G728 16 Kbps
G726 16-40 Kbps
G723.1 6.3 5.3 Kbps
711 is the best then 729 728 726 723.
If you have the bandwidth keep it at 711
if you want to compress and not lose quality 729
Call control
Q931 for ISDN
H225 for the rest.
This is done over the TCP
UDP
G7xx is the Audio over UDP
H.26x H for Hvideo
or RTP real time Protocol does them both.
RTCP is control of the Video/audio
RAS is control
SCCP Cisco proprietary VOIP call cotrol..... IT only sets up the Control
RTP for voip streaming. this is the actual data call stream.
MGCP media Gateway Control Protocol
The HQ Gateway controls everything.
SIP - voip networks for non-cisco proprietary.
IP = 20 bytes
UDP = 8 bytes
RTP = 12 bytes
cRTP compresses the 40 Bytes to 2-4 Bytes
Hop by Hop for small 768 kbps links
MGCP allows the CUCM to control Gateways that go to PSTN
the CUCM is the Call agent endpoints are the phones.
H.323
Terminals are the clients
MCU mixes streams
Gateway converts to PSTn
Gatekeeper - Dial plan + CAC used for multisite distributed CUCM
Gatekeeper works like a OSPF DR and holds the Dial plan.
SIP proxy manages the SIP clients
VAD supresses silence
Propagation delay is the travel time.
Processing delay is the time to convert it to digital
Serailization is how long to put it on the interface. -
Queuing delay is waiting ebcause of other packets. - LFI and QoS helps
Jitter is the change in the delays - use dejitter buffers
Echo delay of 15ms and above must be cancelled.
Classify MATCH
Mark it with the color THEN
Congestion avoidance by using WRED or DWRED to drop tails.
Traffic Policing
Traffic Shaping by buffering and releasing slowly.
AUTO-QoS
Marks
does 802.1Q
LLQ
CBWFQ for control traffic
P>S.
VOICE sucks.
Wait till you have to use the Cisco tools to sell someone a Callmanager.
IPv4
IPv4
Version
0100 = 4 so IPv4
0110 = 6 so IPv6
IHL internet header length.
How long is it in Bytes (IPv4 changes size) (IPv6 is fixed)
TOS Type of service which is your QoS DSCP coloring marking.
Total Length of the packet including the data. Useful for determining if you need to fragment the packet
Identification - identifies the Fragments.
Flags
0 Fragment
1 do not fragment
Fragment offset this is fragment 1 of 40
TTL time to live each hop cuts 1
protocol 8 bits used by IANA
1 ICMP (ping)
2 IGMP (multicast)
6 TCP
17 UDP
50 ESP
51 AH
88 EIGRp
89 OSPF
103 PIM (multicast)
112 VRRP
Header Checksum - used to see if the packet is still ok after transport. Changes every header change.
Source address 32 bits
Destination address 32 bits
IP options not in use. Used for security , route record and similar.
Padding so the packet ends on a 32 bit boundary.
TOS
used for the QoS.
Voip is 101
nothing is 000
PIFFCIN priority imediate flash flash Critical in network
TOS itself is 4 bits.
It can be used to select a route based on.
Money
reliable
throughput
delay
With DSCP they dropped the TOS which nobody used.
The way it works now is Class 4 will have a higher priority.
and if there is congestion the high Drop will be dropped first.
Precedence AF 1 AF 2 AF 3 AF 4
Low drop precedence 001010 010010 011010 100010
Medium drop precedence 001100 010100 011100 100100
High drop precedence 001110 010110 011110 100110
So a 1 at the beginning is better. 1xx
A 010 will not be dropped.
MTU ethernet 1518
LAN jumbo frames
TCp will retransmit
UDP wont'
Class A 0xxxxxxx so 0 to 127
Class B 1xxxxxxx so 128 to 191
Class C 11xxxxx so 192 223
class D 111xxxxx so 224 239 multicast
Class E 1111xxxx so 240 to 255 experimental.
Unicast
Broadcast
Multicast
Private are not routed 10/8 172.16/12 192.168/16
1 class A 16 Class B 256 Class C
You can subnet the addresses above.
Static nat is ONE to ONE private to Public.
Dynamic NAT overloading is PAT port Address translation.
Dynamic Overloading is an internal pool to an external one.
Inside Local is the IP of my PC.
Inside Global is the Public IP I get on the web
Outside Global is the IP of a device on the WWW.
Outside Local is his IP when he is in my STUB/LAN
BOOTP
get IP and gateway using UDP replaced
DHCP
Manual is to map a MAC to an IP address.
Automatic does not expire
Dynamic is from a Pool and expires.
DHCPDiscover.
Router can relay this
DHCP Offer
DHCP request
DHCP acknowledge
DHCPNAK not acknowledge I am out of addresses.
DHCP should be in the server farm / datacenter
Internal DNS campus
Edge External
remote datacenter BOTH
ARP
IPV6
128 Bits instead of 32 bits per address.
Each IP is globally unique
Header is fixed at 40 Bytes
Header will reference options so it is a fixed size.
Addresses can autoconfigure if required.
IPSEC is built in
MTU discovery
Multiple IPv6 addresses
No broadcast replaced by multicast
Version 0110 IPV6 = 6
Traffic class 8 bits = TOS
Flow 20 bits for ordering the flow.
Next Header to add more
Hop limit = TTL
source
destination
6
17 udp
50 esp
51 ah
88 eigrp
89 opsf
ipv4 compatible 000000000x.x.x.x
FF multicast
FE link local
FC private addressing
Global is routable
64 bits netowrk 64 bits host (made up from the MAC 48 bits)
To convert a MAC 48 to 64 you add two FF FF in the middle.
FE is link local can be auto configured
FC is private addressing Unique
Globally aggregetable = aggregate of the IPV6
Anycast is to the nearest.
FF:01 1 all nodes
FF: 01 2 all routers
FF:02 5 OSPF
FF:02 6 OSPF designated
FF:02 9 RIPnG
FF:02 A EIGRP
FF:02 C DHCP
ICMPv6 discovers MTu
IPv6 ND neighbor discovery
IPv6 DNS AAAAAAAAAAAA
Use the same DNS server.
Stateless link local
Stateless global
Stateful DHCP
Global
Talk to router and gets the prefix
Prefix + MAC = address
EIGRP for IPv6
RIPnG
OSPFv3
BGP4
ISIS for IPv6
Dual Stack is both IPv4 and IPv6
Tunneling IPv6 into an IPv4 tunnel
Translate IPv6 to IPv4
Dual Stack - if DNS sends AAAAA it uses IPv6
Automatic Tunnel
IPv4 compatible
6 to 4 the destination has an IPV4 in it which is used as the tunnel envelope
6 over 4 Multicast over Multicast
ISATAP - Greek, Chinese
Daul stack can use PAT or NAT-PT
Ciscio 6PE over MPLS
Service Block service the translations.
Version
0100 = 4 so IPv4
0110 = 6 so IPv6
IHL internet header length.
How long is it in Bytes (IPv4 changes size) (IPv6 is fixed)
TOS Type of service which is your QoS DSCP coloring marking.
Total Length of the packet including the data. Useful for determining if you need to fragment the packet
Identification - identifies the Fragments.
Flags
0 Fragment
1 do not fragment
Fragment offset this is fragment 1 of 40
TTL time to live each hop cuts 1
protocol 8 bits used by IANA
1 ICMP (ping)
2 IGMP (multicast)
6 TCP
17 UDP
50 ESP
51 AH
88 EIGRp
89 OSPF
103 PIM (multicast)
112 VRRP
Header Checksum - used to see if the packet is still ok after transport. Changes every header change.
Source address 32 bits
Destination address 32 bits
IP options not in use. Used for security , route record and similar.
Padding so the packet ends on a 32 bit boundary.
TOS
used for the QoS.
Voip is 101
nothing is 000
PIFFCIN priority imediate flash flash Critical in network
TOS itself is 4 bits.
It can be used to select a route based on.
Money
reliable
throughput
delay
| Class 1 (lowest) | Class 2 | Class 3 | Class 4 (highest) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Drop | AF11 (DSCP 10) | AF21 (DSCP 18) | AF31 (DSCP 26) | AF41 (DSCP 34) |
| Med Drop | AF12 (DSCP 12) | AF22 (DSCP 20) | AF32 (DSCP 28) | AF42 (DSCP 36) |
| High Drop | AF13 (DSCP 14) | AF23 (DSCP 22) | AF33 (DSCP 30) | AF43 (DSCP 38) |
With DSCP they dropped the TOS which nobody used.
The way it works now is Class 4 will have a higher priority.
and if there is congestion the high Drop will be dropped first.
Precedence AF 1 AF 2 AF 3 AF 4
Low drop precedence 001010 010010 011010 100010
Medium drop precedence 001100 010100 011100 100100
High drop precedence 001110 010110 011110 100110
So a 1 at the beginning is better. 1xx
A 010 will not be dropped.
MTU ethernet 1518
LAN jumbo frames
TCp will retransmit
UDP wont'
Class A 0xxxxxxx so 0 to 127
Class B 1xxxxxxx so 128 to 191
Class C 11xxxxx so 192 223
class D 111xxxxx so 224 239 multicast
Class E 1111xxxx so 240 to 255 experimental.
Unicast
Broadcast
Multicast
Private are not routed 10/8 172.16/12 192.168/16
1 class A 16 Class B 256 Class C
You can subnet the addresses above.
Static nat is ONE to ONE private to Public.
Dynamic NAT overloading is PAT port Address translation.
Dynamic Overloading is an internal pool to an external one.
Inside Local is the IP of my PC.
Inside Global is the Public IP I get on the web
Outside Global is the IP of a device on the WWW.
Outside Local is his IP when he is in my STUB/LAN
BOOTP
get IP and gateway using UDP replaced
DHCP
Manual is to map a MAC to an IP address.
Automatic does not expire
Dynamic is from a Pool and expires.
DHCPDiscover.
Router can relay this
DHCP Offer
DHCP request
DHCP acknowledge
DHCPNAK not acknowledge I am out of addresses.
DHCP should be in the server farm / datacenter
Internal DNS campus
Edge External
remote datacenter BOTH
ARP
IPV6
128 Bits instead of 32 bits per address.
Each IP is globally unique
Header is fixed at 40 Bytes
Header will reference options so it is a fixed size.
Addresses can autoconfigure if required.
IPSEC is built in
MTU discovery
Multiple IPv6 addresses
No broadcast replaced by multicast
Version 0110 IPV6 = 6
Traffic class 8 bits = TOS
Flow 20 bits for ordering the flow.
Next Header to add more
Hop limit = TTL
source
destination
6
17 udp
50 esp
51 ah
88 eigrp
89 opsf
ipv4 compatible 000000000x.x.x.x
FF multicast
FE link local
FC private addressing
Global is routable
64 bits netowrk 64 bits host (made up from the MAC 48 bits)
To convert a MAC 48 to 64 you add two FF FF in the middle.
FE is link local can be auto configured
FC is private addressing Unique
Globally aggregetable = aggregate of the IPV6
Anycast is to the nearest.
FF:01 1 all nodes
FF: 01 2 all routers
FF:02 5 OSPF
FF:02 6 OSPF designated
FF:02 9 RIPnG
FF:02 A EIGRP
FF:02 C DHCP
ICMPv6 discovers MTu
IPv6 ND neighbor discovery
IPv6 DNS AAAAAAAAAAAA
Use the same DNS server.
Stateless link local
Stateless global
Stateful DHCP
Global
Talk to router and gets the prefix
Prefix + MAC = address
EIGRP for IPv6
RIPnG
OSPFv3
BGP4
ISIS for IPv6
Dual Stack is both IPv4 and IPv6
Tunneling IPv6 into an IPv4 tunnel
Translate IPv6 to IPv4
Dual Stack - if DNS sends AAAAA it uses IPv6
Automatic Tunnel
IPv4 compatible
6 to 4 the destination has an IPV4 in it which is used as the tunnel envelope
6 over 4 Multicast over Multicast
ISATAP - Greek, Chinese
Daul stack can use PAT or NAT-PT
Ciscio 6PE over MPLS
Service Block service the translations.
Thursday, February 28, 2013
WAN design
Circuit Switching - the circuit comes up for the duration. Phone and ISDN
leased lines - dedicated to you by the service provider TDM T1
Packet and Cell - Frame and ATM
Hub and spoke to the HQ. However if the router at HQ fails all are affected.
Full mesh - expensive to maintain. N(N-1)/2
Partial Mesh - flexible to where you want it.
VPN over public networks is limited to a Best effort as you cannot control the traffic in the ISP
Access VPN for users- You can also use a NAC to connect to first which will then set up the VPN
The NAC is a public facing device Portal where you http to it and then type a user password.
Intranet VPN - this is from site to site. Using public or WAN.
Extranet VPN is for business partners so they can access the DMZ
Enterprise VPN is when you set it up.
IPSEC is one VPN usually from firewall to firewall.
It can use ESP to encrypt the data or AH which only encrypts the headers (not secure for data)
HMAC codes in it will protect from man in the middle attacks and replay.
You can also use PKI certificates for an added layer.
Cisco Easy VPN - you set up a server which is the head. Then the remote configuration is easy.
the remote devices are ISRs.
GRE - works for encapsulation all protocols. Does not have any security.
you must add IPSEC tunnel to it in order to have security.
DMVPN - dynamic VPN
NHRP next hop resolution protocol which will point to the HQ.
mGRE Multipoint GRE supports multipoint tunnels.
IP multicast , routing , dynamic spokes all QoS
Each remote site is connected using a GRE tunnel to the HQ.
For redundancy you will need two heads.
DPD dead peer detection can be used to verify tunnel is alive (keepalive)
VTI virtual tunnel interface
Can run routing , does not need GRE or mGRE.
L2tpv3
can run frame relay and ppp ethernet
Service provider VPN.
Can run MetroEthernet
VPLS is a VPN over MPLS
it allows you to run Layer 2 from one location to the next.
Useful for Storage redundancy for example.
MPLS
Uses Labels instead of routing and can run over a variety of media.
Uses VRF
Layer 3 MPLS Tight SLA and QoS.
VPNs are flexible and cost effective.
Dial Backup used for ISDN so it will ring a floating route.
Secondary WAN link - backup or load sharing.
Shadow PVC - used in frame relay.
IPSEC VPN backup tunnel can be used in case the ISP MAN fails.
Load balancing.
Cna be per packet. usually 56kbps or below.
Per flow or destination is better. also called fast switching.
Decision influence.
High Availability - backup power, backup devices, backup WAN
Growth
Expenses -
Complexity - Metro is easier.
Cost to implement -
Network Segmentation to separate traffic.
Voice and Video QoS.
Private WAN - Frame relay and ATM . You own lease the circuit
ISP WAN - basically the internet
SP MPLS/IP VPN - they are good
Private WAN with MPLS - jeez hiring some CCIE's to maintain it is expensive.
considerations
Port Density
Port Type
Modular
throughput
REdundancy / Supervisor or power
Future growth
Software
Bandwidth
Security
ISR can do wan video , voice, security
800 ISR remote user
1800 ISR branch
7200 - 10000 medium routing
7600 high end routing
12000 CSR - service provider grade.
29xx 35xx 37xx are access switches.
45xx chassis
65xx high end chassis.
Router - WAN
Switch LAN
Security appliance at the branch
AP wireless for mobility
CUCM for voice
IP phones and desktops
Small office 50 users 1 TIER
medium office 50-100 2 tier
Large 100 + 3 tier
ISR G2 is better
Small can use an ISR with ports or one switch.
Medium branch redundant routers.
Switches with Stacking.
Large Branch
Dual links
Dual routers
Dual ASA
Dual switches with stacking.
ISR 800 for teleworker.
WAN technologies
WAN
Requirements are
SLA
bandwidth
latency
loss
Cost
utilization.
Goals and policies
Applications and growth
budget
ISDN
BRI - 128kbps
PRI is 1.54 Mbps like a T1.
DSL mainly Async DSL
Cable Cable Modem Termination System CMTS
Wireless
Bridge is point ot point
LAN is 150 - 300 Mbps max
MObile GSM , GPRS ,, UMTS 3G , LTE
FrameRelay.
PVC permanent
SVC switched just for the duration.
Sonet Circuit baed.
OC 1 51
OC 3 155
OC 12
OC 48
MPLS
Goal is to use labels instead of routing tables.
CE--> PE--> P __> p --> PE--> CE
Dark Fiber is Point to Point
DWDM runs on the SONET and increases the ability to split ligh Lambdas.
CIR Commited infra
Burst above
Same PPDIOO
Prepare
plan Desgin
implement operate
optimize.
Voice 250 ms
Video can afford to lose some pakcets voice CAN'T
Private Dark Fiber
Leased TDM sonet
Shared MPLS framerelay.
Fixed cost equipment and setup
recurring are the monthly charges.
QoS
classify it based on protocol or a matching ACL.
Classification orr coloring.
Congestion management
Link Efficiecy for low speed to reduce latency and jitter
traffic shaping use ingress and egress flows.
Classification.
Identify and mark. = classification
NBAR can use layer 7 to recognize applications and then label them with a priority.
CAR commited access rate. -- Basically match a traffic and then apply a priority
Congestion management
FIFO first in first out
PQ priority queiuing sets up 4 levels.
however LEVEL High must be emptied before any of the other three are allowed.
So if you have too much traffic at level High , the other traffic will suffer badly.
Custom Queuing 16 Queues, you can set up the queue limit.
so when it is full. The other queus get serviced.
WFQ - this is for interfaces below 2.0 Mbps .
it creates two queues - high bandwidth. low bandwidth.
low gets service first.
Class Based Weighted Fair Queiuing.
SAme as WFQ but you can use access list and it is modular.
LLQ
Low Latency Queuing.
Basically class based weighted fair queuing + PQ.
So voice EF gets serviced first + there is a limit on it.
Traffic Shaping.
Slowing down traffic so the utilization is high but consistent.
helps to curb bursts into longer flows.
Policing.
Dropping traffic that passes a limit.
'Link Efficiency.
LFI link fragmentation and interleaving - breaks up large packet flows and puts small voip in between
MLP multilink PPP bonds links like 2*T1
RTP real time transport. Compress the RTP header from 40 bytes to 2-5 Bytes.
Window Size.
Extend the Window size to allow more data in before you have to send an acknowledge.
Wednesday, February 27, 2013
Wireless LAN
802.11 1mbps 2mbps dsss
FHSS frequency hop will hop from 1 to 2 so doubles the bandwidth.
802.11b 11mbps uses 11 channels
802.11a 54 Mbps 13 channels on UNII not compatible with 802.11b
802.11g 54 Mbps ISM compatible with 802.11b
802.11N can run on both 600 mbps MIMO multiple in multiple out and OFDM to send the data.
ISM uses 900 2.4 and 5.5 only 2.4 is used for 802.11b g n
UNI uses 5.0 ghz and is for 802.11a and 802.11n
1 6 11 do not overlap.
SSID is used, this is similar to a VLAN to segment the networks.
CSMA /CA collision avoidance.
WEP is insecure
WPA allows you to add security 802.1x and AES
MAC adresses can be spoofed.
EAP-FASt Flexible authentication can be used for the connection.
VPN IPSEC can be used to segment the traffic to the HQ.
802.1x uses EAP and Radius to verify your access.
LEAP uses a radius and 802.1x
Cisco
IDS and firewall to control the traffic.
Cisco UWN unified wireless network.
Client devices laptop
accesspoints cisco AP
Network unification like QoS IPS RF management all of this is done by the controllers.
network management can be done using the WCS server
Mobility services like guest , Voice , threat detect.
benefits.
reduce TCO
enhance visibility
manage the RF (cleanAir)
Security Controller
Unify the wire and wired-less
enhance collaboration.
LWAPP is what the APs use in order to connect to the controller.
AP to WLC
Layer 2 LWAPP controller must be on the same subnet Ethertype 0xbbbb
Layer 3 LWAPP controller can be on a different subnet. 12222 12223
12222 data 12223 control
CAPWAP is the newer one.
Uses AES to secure the com
MTU discovery
Control 5246
data 5247 so the opposite
Split MAC - Lwapp
the AP does
Beacon 802.11
802.11 control
802.11e queue and piroritization
802.11i encryption
The Controller does.
802.11i security
802.11 mac management
802.11e reserve resources.
Local MAC - CAPWAP
802.11 MAC management so the AP does this instead of the controller.
Controller can also proxy.
AP modes
Local Mode - the usual
Hybrid - it will reside across the WAN H-REAP
Monitor - cycle every 60 and do not participate. Used for IDS. Location based.
Rogue Detector - sits on the Trunk and checks if there is a rogue device
Sniffer mode- captures packets and sends them to a Sniffer Airopeak.
Rogue detector gets a list of MACs they hear from other devices.
If that MAC is on the WLC then the rogue detector will let you know.
Bridge mode is for MESH
Connection Lwapp.
Send Lwapp Discovery.
1. local subnet
2. Get WLC from other AP
3. previously stored WLC address.
4. DHCP option 43
5. DNS CISCO_LWAPP_CONTROLLER.local.domain.
WLC will answer
AP gets list of WLCs
Selects AP
1. Previously configured.
2. Master
3. most available.
AP to WLC join
Capwap
does capwap
no response 60 seconds does LWAPP
no response start again.
First
Second
Tertiary
Master
most available.
Supplicant is the client.
WLC is the authenticator
Radius is the Authenticating server.
To WLC is capwap
from WLC to Radius is EAP extensible authentication protocol.
EAP- TLS public key.
EAP - TTLS certificate only on the server.
PEAP - Cisco + mschap.
LEAP - Cisco plus the CCX extensions.
EAP-FAST build a tls tunnel
WLAN is an SSID
Interface maps the VLAN to the SSID
port is a port.
A port goes to the switch
you can use many ports and etherchannel them.
Management interface. - Used for L2 Lwapp. Connection to radius. In-band management
Service port - used for out of band management. Statically configured.
AP manager - L3 discovery static
Dynamic interface - is to map the VLAN to WLAn
Virtual interface - DHCP relay , mobility
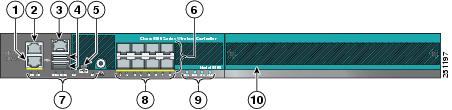
So port 2 is a physical port.
You configure it as the SERVICE port. It is for out-of band management.
Ports 8 can be aggregated LAGed and will go to a switch.
Sorry, best I can do.
Service Port. is a totally separate port for out of band servicing.
Management port is the in band and old Layer 2 LWAPP.
AP manager is for Layer 3 LWAPP.
Dynamic ones are for each VLAN WLAN they will change dynamically.
Virtual is to connect to another WLC and transfer mobility. So you can ROAM from room to room or building.
2100 25
ISR 25.
So far easy.
3750 Switch with contorller built in 50
4400 100
6500 WLC module 300
5500 500
Intracontroller
ie the same controller.
So no chaneg except you moved IPs.
Inter controller Layer 2.
From one controller to the next
Just moves the MAC from WLC1 to WLC2 database.
A mobility message updates the controller.
Inter controller Layer 3.
From one IP subnet to another.
WLC 2 Creates a shortcut. An ANCHOR and tunnels the data back to WLC1.
Mobility group will create the anchor and tunnel.
Up to 24 WLC s
UDP 16666 unencrypted
UDP 16667 encrypted.
Minimize intercontroller roaming.
less than 10 ms
Layer 2 is better
Detrministic redundancy
Primary secondary tertiary.
Dynamic
Easy and load balance.
N+1 one controller is backup
N+N same number of controllers as the ones you have deployed.
N +N + 1 same number of controllers as you have + tertiary as spare.
Limit to 20 users
7 voWLAN
RRM radio resource management
Adjust RSSI
balance the clients
RF group is a group of WLC that sync their RRM
80 signal will elect a master to set up the strenght
Neighbor messages
EoIP for guests
All the guest traffic goes to one WLC. an anchor WLC.
Mesh
RAP is Root
MAP is not connected to the wire
Four hops max of 8
throughput drops every hop by 50%
20 MAP per RAP max of 30
1100 internal 3500i internal
1200 3500E external
branch
300 ms or less
use H-REAP for WAN
LOCAL mac
allows you to work even if the WAN is down.
REAP
extends lwapp timers.
Layer 2 security limit
H-REAP
Allows NAT
Datacenter design
So unified computing will be the UCS line.
Unified Fabric will be the NEXUS line. Fcoe MDS for Fibre and CNA converged adapters
Virtualization is the Vmware/Windows/Citrix Nexus 1000V sits on a vmware Vlan Vsan
Virtualized Servers on the UCS
Virtual resources.
FC or FCoE or iSCSI
Vlan or VSAN Vsan is for Fibre.
and virtualized storage and network. You can have context on firewalls, VSS or VDC
Forces that impact are
Power
Rack Space
Cooling
Management
Security
ILO can help manage servers remotely, you connect to ILO and manage it as if you are there.
Space
Load on the floor
power cooling
cabling - blade servers reduce cabling
HVAC heating ventilation and cooling.
Architecture.
Floor load
Space
Power cooling
cabling
Environmental are
Humidity
temperature.
physical
Access to site
Fire supression
Security alarms
Capacity
space for employees
Compliance
PCI SOX Sarbannes oxley. HIPAA
Power
Cooling is the most.
Servers
Network
Converting from 220 to 110
lights
1 Watt = 3 BTU
Access
provides ports
Allows for nic teaming and etherchannel
Allows for layer 3
mix oversubscription.
Distribution.
SSL and IPS
use modules in the 6500
GLBP security
place the ROOTs if you must use STP.
Core
Layer 3
Multicast
Low latency switching
Distributed forwarding using daughter cards.
10 gigE
Scalable multicast.
key drivers for virtualization
Cost
reduce device count
Isolate users and traffic
Better performance for price ratio
higher utilization
better uptime
Virtualization network
Vlans are virtual broadcast domains on a switch.
Vsan are virtual on a storage switch like Fibre MDS
VRF virtual routing and forwarding create a virtual forwarding table (MPLS mainly)
VPN create virtual networks over the same media
vPC virtual port channel this is MLAG on the Nexus 7000 pretends to be one link
Device itself Virtualization.
VM virtual machines on the ESX
ACE context splits ACE
VSS virtual switching system on the 6500
ASA context split firewalls
VDC virtual device context. used on the NExus 7000 pretends to be separate switches entirely.
Access control at the access layer. classify the users/devices
Path Isolation like VPN or VRF logical separation over the same media
Services split using the firewall to control the network Vlan to vlan traffic. control and manage
Enterprise LAN
802.3 is the IEEE for ethernet base-T
distance is 100 meters for copper
802.3U is for 100 Mbps
Base-TX is the CAT 5
Base-T4 is for Cat 3 full duplex is not possible.
base-FX is fiber
Class 1 repeater 1 hop
Class 2 repeater can have a max of 2 hops.
gig is 802.3z 1000 Mbps
802.3ab is 1000 Mbps over copper CAT cables.
In general 100 meters for cat cables
550 for multimode
Single mode can go 10 40 or 70
SX is multimode
LX is singlemode / multimode
CX is coax like the antennas cables.
802.3ae is 10GigE
SR is multimode
LR is multi/single
er is single 40 KM
ZX is 70
10gbase-t is 100meters
Etherchannel can bundle links.
So if one fails the other ones still send data.
Links must be same speed, same duplex, same vlan or trunk
The tables in the book are antiquated.
Repeaters - dead , they repeat the signal can't have more than 5 segments 4 repeaters 3 populated.
HUbs are a single broadcast domain , single collision domain . they are dead too.
Bridge is a switch that is using software. 2 or more collision domains
Switch is a bridge that uses hardware chips to forward the data. So more ports and faster.
Each port is a collision domain . Each Vlan is a broadcast domain.
Routers remove the L2 and add their L2 . they work on layer 2
So each port is a broadcast domain and a collision domain.
repeater + hubs work on bits.
Bridge + switch work on frames
L3 switch + router work on packets
LAN design
Network characteristic is the application protocol
Infrastructure charactersitics is the L2 L3 switching routing
Environmental characteristics are the geography and distances.
Peer to peer messaging
client local 80% is local 20% goes out.
Client server farms 80% is south to north 20% is internal.
client to enterprise edge. like exchange or other public servers in the Internet Edge.
Client to server farms has the highest cost and reliability required.
Best Practices.
Access Layer
Limit Vlan to the Rack. -so you can layer 3 from the access layer.
use RSTP as it is better than STP faster times.
Set trunks to ON on no negotiate.
Prune unused vlans to minimize the traffic.
use VTP to sync the vlan database.
Use PortFast and label host ports as access ports.
Consider putting Layer 3 at the access to improve load balancing and convergence.
Use switchport host to enable portfast on ports so they go to forwarding quicker.
Use Cisco tools.
1. portfast skip learning and listening.
2. loop guard b so the port won't switch to forwarding and create a loop.
3. root guard to mark that port as one that will not allow a switch there to become root.
4. bpdu guard to disable the port if someone connects a switch.
Distribution layer
Qos Security filtering policy and redundant links.
If you use L2 then use HSRP, VRRP, GLBP
Use Layer 3 if you can to improve convergence.
Peer on links that will transit data.
Build triangles and not square.
Try to keep layer 2 vlans in the distribution instead of sending them to core.
summarize routes to offload that from the core.
use VSS to eliminate STP and HSRP
VSL is the VSS link.
Core layer
Use layer 3
Use same cost links
Use routing
use triangles.
Each building should have the addresses summarized.
Medium size is two layers 200-1000
Distribution and core are collapsed.
Small
One layer.
Server connect.
Single Link NIC
Single NIC two ports one to each switch then you bond then in an etherchannel
Two NICs going to TWO switches.
Content switches.
Datacenter 3.0
Load balancer
SSL offload
Firewall
IPS
At access layer you can always stick a QoS classification.
VLANS
ISL is cisco it tags before and after the packet.
802.1Q is Vlan it marks it inside the packet.
802.1P uses 3 bits for Priority.
Mark 802.1P as close to the source as you can.
Multicast.
To avoid flooding the hosts use.
CGMP Cisco
IGMP iEEE
CGMP the switch will query the router for the MACs of recipients.
IGMP the switch listens to messages from the hosts to the router like join or leave
CCDA models
Hierarchical models allow you to.
save cost
Make it easier to understand
Modular network growth
Improved fault isolation.

core
* fast
* highly reliable
* redundant
* fault tolerant
* Low latency
* Avoid CPU intensive and classification
* QoS using the classification done by other devices.
* limited diameter hop
Distribution
*aggregate
* filter
*route
Access
* classify QoS
* Rate limit
* arp inspection
* PoE
* Trust
In this model, the Distribution handles the RVI or IP of the Vlan and will route between vlans.
Because of STP one link is disabled from the access to the distribution.
So you are paying a load of money for a "backup link"
If you drop the Layer 3 border to the Access layer.
Then you will gain more links.
However the Layer 3 licenses cost more.
You will also be limiting the Vlans to be local to the switch.
Cisco 6500 VSS- supervisor 720-10G
can run VSS.
VSS is proprietary to Cisco and makes the switches pretend to be one switch.
Must use VSS capable Sup720 or SUP-2t.
The above was the simple model.
This is the Enterprise Architecture Model.
Let's have a look.
Basically the old model was the Core---<>--- Distribution----<>---- Access.
Since now we have a dedicated Datacenter we can also expand it to
Core----<>---- Datacenter Distribution -----<>----- datacenter access layer
For the WAN we can also create an Edge Distribution and an Enterprise Edge (access)
So in reality our network looks like 3 triangles
The smaller the network the more layers you can consolidate.
Enterprise Edge.
In this case they split Ecommerce and Internet into two modules.
The E-Commerce will have
Firewalls - obvious
IPS and IPS on switches - IPS is the new must
Web,application and database - for Ecommerce
Internet
Will have firewalls
Http servers
Ftp
DNS
WAN
Will have MPLS/Frame/VPN site to site which you can use
to connect branches or to datacenter
Remote Access VPN can use PSTN dial up
or the Internet to allow VPN access for users.
Connecting to your provider.
one router does not provide local router redundancy.
One ISP does not provide ISP redundancy.
Entyerprise WAN technologies.
MPLS multiprotocol label switching
Metro Ethernet using QinQ
Leased line
SONET , SDH
PPP
Frame Relay.
ATM
cable/DSL
Wireless
Cisco says MPLS will map the DSCP QoS marking into the relevant MPLS
Service Provider Edge.
Matches your Enterprise Edge module.
Enterprise Branch Office.
Usually a router and a switch.
The connection back to the Enterprise Edge can be
1. MPLS using the WAN
2. VPN to lower the cost using the INTERNET
Enterprise Data center or Cloud
Teleworker is a very small office or one person.
Usually you can use an ISR or an ASA to collapse everything into it.
Borderless pillars are.
Access layer High availability.
Workstation to Router
Server redundancy in the FARM
router redundacy within the network compenents
Link media in the access layer.
Workstation path discovery can be using.
ARP - find out the gateway
VRRP HSRP GLBP all are the same two devices create a virtual gateway.
ICMP router discovery
VSS - this is the two chassis that behave as one
Explicit - I can explicitly configure the gateway manually on the NIC>
RIP - yes you can run RIP on the Server ?? not the smartest
HSRP
VRRP is the same thing as HSRP except it is not proprietary.
GLBP is the Cisco improvement.
It allows BOTH links to stay active thereby increasing the available bandwidth.
Load Sharing
Multiple Routers up to 1024 Virtual Groups on each interface.
You an PREempt a router with a higher priority.
Authentication can be used.
Server redundancy
Use
FEC and GEC etherchannel bundles.
Use Dual NICs
Load balancing in Cisco can be changed by.
maximum-paths this will change the number of links the router will use from the default of 4.
Maximum is 6.
All links must have the same cost in order to load balance.
EIGRP can use Variance to load balance (bullshit)
Process switching load balances packet by packet.
Netflow Switching load balance by destination which is much better as the packets will not have a chance
to come out of order.
Mesh is N(N-1)/2
Full mesh
Keep broadcast at less than 20%
Make sure a Backup redundant link is not using the same last mile circuitry.
So
Workstation to Router use HSRP,VRRP, VSS
Server redundancy use daul attach NIC , FEC, GEC bundles
Route Redundancy use the load balancing and high availability of more than 4 routes
Link Redundancy use a variety of WAN.
Tuesday, February 26, 2013
CCDA exam intro
CCDA exam.
Have some free time. So I'll just pass it.
Foundation.
PPDIOO
Prepare
Plan
Design
Implement
Operate
optimize
So far so good.
The test revolves around acronyms so memorize.
Business forces that will impact your design.
ROI - Return on investment
Companies expect either savings or improved earnings due to the devices you place.
Let's cough up an example.
Let's say I have 8 switches in my rack.

To manage them I need to connect using telnet/console to the switch and give it some commands.
Let's say I need to upgrade them. Then I would need to spend 20 minutes * 8 = 160 minutes
on an upgrade.
Let's say I want to troubleshoot the switches, then I would need 8* more screens and command typing to get the issue resolved.
You can calculate the cost of IT engineer as $50 an hour and start adding it up.
now to save money in the above example. I can convince management to purchase a
Cisco 6513 chassis.

Now, I only need to upgrade one supervisor and troubleshooting becomes easier.
So I am saving money.
The ROI is calculated by measuring how long would it take to recover the investment I just made
on the chassis.
Another way to look at ROI is by looking at the benefits of an upgrade.
Let's say the users spend 5 minutes every day till the Outlook syncs and another 5 minutes
a day wasting time waiting for files to get copied.
10 minutes * $6 an hour * 600 employees = $600 dollars of wasted time staring at the screen.
Now if I upgrade them to 1000 instead of 10/100 then they will spend 5 minutes waiting.
So 5 minutes * $6 an hour * 600 employees = $300
So if I upgrade them to 1000 Mbps switches and network cards I will be saving $300.
So 20 switches * $10000 each = $200000
Now your ROI break point or the point at which you start making money on the upgrade is
$20000/$300 = 660 days
So if I invest in upgrading the switches the company within 2 years will have made back the cost
and will be making money on the investment.
A good salesperson will easily be able to demonstrate the value and not just say
we need 1 GigE switches (1000Mbps) because they are pretty or fast.
{good salespeople are hard to come by}
Regulations
Because of companies like Enron and crackers. There are new regulations in the market.
HIPAA Health Insurance Portability Accountability Act. -
You me and everybody has a record of their visit at the Doctors, well I might have an erection problem.
Now I wouldn't want it to be published on the web when you google saar that I appear as having that.
So in order to protect the confidentiality of my medical information and transactions.
HIPAA came along with guidelines, so the Dr. needs a safe system. When he connects to my insurance
he needs to have a secure VPN. When they store my data their Database needs to be secure. etc
The second example is Visa and banks. If I can hack into a computer at a retailer that does Visa transactions
I can copy the numbers and Secure codes in the back and then go shopping!!!!!
So for that you have the PCI DSS Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard.
So now my Amazon shopping is secure and I can safely swipe my card.
The third good example is Sarbannes-Oxley. This gem was passed following Enron collapsing
without anyone having seen even a hint. It talks about auditing and how you should "measure"
kpms key performance indicators in IT.
So for us it means we have to monitor the network at Amazon, because if it collapses then the
stock goes down the toilet. So now business must track and publish KPMs so their stock owners
can asses the health of the company.
All in all, when you are selling. You can throw those around in order to get the client to be MORE secure
Competitiveness
So let's say I have a warehouse with dolls. Now my competitor just built an ecommerce site.
So now he has an advantage. To match him I must build one.
Let's say he is using two internet providers so when a storm hits I am out of business and he is running
around stealing my clients.
So now I need a more powerful router.
These three are the Business Drivers according to CCDA.
Technological Drivers
At the same time there are simple Technological drivers.
Removal of Borders
Back when I started in IT if you worked for an ISP you got a free Frame relay for home.
(this was in Dial up days). So I could work from home to solve issues.
Today with the Iphones, wireless, laptops etc. People want to work from everywhere. On the road
at the airport, at home when sick, etc. So there are no more borders. You need to give them more and more
access.
To address this you will add VPNs, remote access, tunnels etc
Virtualization
Most servers in the enterprise are no longer stand alone. Companies placed them in Virtual Servers which run on top of a Hypervisor. Vmware is one example. The Hypervisor will have 50 VMs running on it.
This leads to a very high utilization rate of the resources and a lot of flexibility.
In order to address this you will probably have to upgrade the network because storage traffic takes
a lot of resources and requires low latency.
Growth Of Applications
so yeah, back when I was a kid 1 channel was all we had on TV. Then two , 20 and now you have
800 channels, streaming VOD etc. All of this requires more and more powerful servers and networks to handle it. The programs over time also become more complex.
If before I was happy word typed a letter. Now I want graphics and links and Visios embedded etc.
So more more more horsepower from the PC and the network.
So
Business drivers are usually driven by business people.
technological ones will be driven by IT asking for resources.
IT optimization can be divided into three type.
Datacenter - ie servers, infrastructure
Network - LAN and WAN
Applications - upgrade the software on them and the application.
Each one has their own people.
Datacenter would be Dell, IBM, HP inclined people.
Network - would be CCIE's Juniper etc.
Applications - are usually programmers and software people.
You can no longer master all three unless you are in very SMB .
Cisco has created a FrameWork.
A framework is a patch of ideas or guidelines to help you talk the same lingo to other people
in the field. Which is very important. I might be peddling eggplants and the other guy is british so he is talking about Aubergines. So in the end we fail to make Baba Ganush .
As you can see there are areas
where they will intersect.
Cisco Borderless
anywhere, anytime,anything,anyone
lot's of A's
So from anywhere you go(abroad) , at anytime you want (late), anything you want (like outlook), anyone (let's say my business partners)
It also needs to be secure (VPN) , reliable (high Availiability, clusters) , seamless (one login)
It will be made from 4 Blocks.
Policy and Control - You can apply policies anywhere, if you are at home or you just came to the office
Network Services - these are services for the network, like control or energywise
User Services - like mobility , performance (acceleration), Security (vpn)
Connection management - manage the connection security everywhere.
Collaboration
Alright we got a nice network but money is made as a team effort. I need to talk to sales, they need to
talk to shipping, shipping to fed ex.
For all of this to happen you need collaboration software.
Communication and collaboration applications - telepresence (video conferencing), Email, etc
Collaboration Services - these are services for the layer above for example PRESENCE
so I know if the user is online, then I can chat him
Infrastructure - this layer provides you with the tools for the two above.
It includes virtualization , storage, network
Datacenter
Cisco builds on the Datacenter 3.0
It's a comprehensive Cisco solution to help with this.

they basically have entered the Hardware for the Datacenter market and the networking of it.
The benefits from the
Framework
are
Functionality - they support the requirements.
Scalability - they allow room for growth
Availability - reliable and anywhere anytime.
Some more examples are.
Performance - less latency, more bandwith,
Manageability - easier to use , easier to detect faults.
Efficiency - the cost is reasonable
The architecture is roughly.
Switches/ servers (nuts and bolts)
They are all easier to control with the cisco UNIFIED fabric,network and computing. (software)
They result in better energy , workload, efficiency
and allow you to virtualize, cloud, automate and consolidate (high level)
Alright,
back to PPDIOO
Prepare
Plan
Design
Implement
operate
optimize.
Keep drilling that cycle that Cisco recommends.
The benefits of using it are.
Lowers the Total Cost of Ownership TCO by validating and planning
Increases availability by producing a sound design and validating it.
Improve the business agility by establishing business requirements and strategic technologies.
Speed access to applications - byimproving performance,availability reliability, scalability.
Actions that lower the total cost of ownership are.
identify and validate the technology - for example identify you need a chassis and test it
plan for infrastructure changes and growth - for example the chassis will be flexible on the line cards you add
Develop a sound design with business goals - a business goal can be more reliability which the
chassis will handle with Dual Supervisors.
Accelerate the implementation - less downtime due to solid implementation.
Improve the network and management - make it easier to manage.
reduce operating cost by improving the process - for example the chassis allows for easier management
Actions that increase availability are.
Asses the network - so it can withstand the traffic.
Specify the hardware and software and keep it current by updating the software (smartnet)
Produce a sound design - so it won't collapse
stage and test -- to make sure it works in your network and not just on the datasheet
Improve staff skills - so they will know what to do.
Proactively monitor the network - so you can predict growth and problems
Proactively manage the security - so you can block breaches and remediate breaks.
Actions that improve business agility
establish the business requirements.
ready the sites and the people
Integreate the technical aspect and align it with the business requirement.
expertly install
continually monitor it
Actions that accelerate the application and services
assess the network
improve the service delivery
improve availability
Manage and resolve problems and keep everything up to date.
As you can see this is a cycle.
Prepare
This phase is where you come up with the Business case.
The business case creates a justification for the expenditure of time and money.
Technologies that support the architecture you are planning will be considered.
Plan Phase.
Here you drill down and identify user needs and goals.
You will also assess the network and see if there is a GAP against best practices and documentation.
You will develop a PROJECT plan with the resources milestones and identify the resources
for the design phase.
Design Phase.
Based on the previous data you gathered and in allignment with the business goals
you will produce a detailed design.
The design will include the Visio diagrams and equipment list.
You will also make the project plan more granular.
Once the design is approved you move to implement it.
Impelentation phase.
New equipment is set up and configured.
Changes should be brought up in change meetings to minimize downtime
Each step should have.
1. description
2. Detailed implementation
3. time to implement
4. guidelines for rolling it back in case of failure.
5. changes must be tested to validate them.
Operate phase.
At this stage you operate the equipment.
Day to day work along with accumulating data for the next stage.
Optimize stage.
At this phase you use the data from operations to see if there is room for improvement.
Also you analyze any problems.
If there is room for change.
You can start the Prepare phase and place a business case for improvement or change
which will start the cycle again.
Since this is CCDA concentrate on the first three stages.
Step 1 Prepare - identify the client requirements as far as business and give a conceptual architecture.
for example : the client is complaining about latency. So conceptually we will look at Nexus 3000
Step 2 Plan - Come up with an assesment of what he has now and the weakpoints or adjustments.
come up with a project plan to move ahead.
Step 3 Design - come up with a detailed design plan and granular project plan
When you run the prepare.
Talk to business managers and to department heads and users to see WHAT they need
business wise .
You can use the
1. Identify the applications and services. -example exchange and outlook.
2. Define the organizational goals example we want outlook to be more responsive and robust
3. define organizational constraints example we have a low budget.
4. Define the technical goals example improve latency by 30%
5. Define technical constraints example the switches are eos and outdated.
You can help yourself by using a template.
now you will have all of the applications identified and the requirements of them.
So the organization wants us to improve the performance of outlook.
now you can identify organizational constraints
For example. The IT goes on holiday for a month.
We lack a high budget - so maybe we get pre-owned.
HIPAA mandates we use IPSEC security for the VPN (which slows down a VPN)
Technological goals is where you can set the deliverables , like reduce latency by %
technological constraints can be cabling issues. Sites. legacy equipment
So far so good.
This is all in the Prepare.
Characterizing the network.
Simply go and ask for any current documentation.
Then validate the documentation to see it is relevant and add more detail.
After that you can run analysis tools to gather data on traffic and protcols.
Site, lan , wan ,power, cabling, rooms
Use existing documentation
Existing tools
or buy new tools.
Cisco Works can give you hardware and software.
make it pretty granular.
Device type - model -software on it - configurations - data from tools - speeds -CPU/mem - WAN data
This can be quite extensive however it can help for building a better design.
Tools
Cisco Works - maps the network and collects the hardware and software
Netflow - gives you data on the traffic.
NBAR - analyzes the application flows.
Third party tools -
Additional tools can be used for example for wireless.
Airmagnet - can analyze interference.
Commands for Cisco.
show tech-support gives you a detailed output
show process CPU - gives you a CPU reading
show version - will show you the IOS you are running.
show process memory - gives you the memory usage.
show log - will give you errors on the log
show interface - will give you stats on the interface.
show policy-map interface will show you policy maps on it.
show running-config will give you the configuration so you can assess the current network design.
show ip cache-flow
will give you the netflow output.
CNS Cisco netflow collector engine collects netflows from devices.
Checklist for best practices
Nework LAN should use switches and not hubs.
no WAN link is saturated anything above 70% is a red flag.
Response times should be less than 100ms or 2ms in the LAN.
Segments should not have more than 20% broadcast /multicast
Ethernet should not have more than 0.1 percent collisions (high utilization leads to collisions)
CPU of more than 75% for more than 5 minutes is a red flag.
output queue drops should not exceed 100 for an hour
Input queue drops should not exceed 50 for an hour
buffer missed 25 per hour
ignored should not exceed 10
QoS should be configured for VOIP or other sensitive traffic.
Steps were
Documentation
Audit of the network - cisco works
Traffic analysis - CNS analyze netflow.
Designing the network.
In order to validate the design you can use a
Prototype - which is a separate network test. (in a lab)
Pilot - a test run on a live network (for example only in the IT department)
Design from the TOP of the model down.
Application needs
then only the transport network and data link physical
Top - Down is more time consuming however more reliable.
Bottom - up relies on experience but can be prone to error.
Design Document -
This document details the business requirement + conceptual design.
The current network and gaps.
Then the design plan, configuration and testing.
1. Introduction - sometimes called the executive summary.
2. Design requirement - that are the business ones
3. existing network - add diagrams and data accumulated from the audit.
4. Design - and why it solves the requirements and addresses the current
5. Validation - data on the testing that was done. also called Proof of Concept.
6. Impelentation plan - for the Staff on how to impelement the design.
7. appendixes with all the detailed data gathered.
Before you move on you need to create a detailed implementation plan.
1. Step
2. reference to the design document
3. detailed implementation of the step.
4. detailed rollback.
5. estimated time to complete.
Q&A
list the PPDIOO
Prepare
plan
design
implement
operate
optimize
which business forces affect the design.
ROI
REgulations
business competitivenes.
efg
Which step is critical in identifying the organizational goals.
Identify customer requriements a
What needs to be obtained prior to designing the network.
Organizational goals
technical constraints
existing applications
bce
Match each PPDIOO with
i implement installation and config
ii optimize proactive management
iii design provides HA design
iv prepare Gap analysis
v operate day to day
vi plan Establish requirements.
Which borderless architecture provides mobility.
User services provide mobility
Which are three steps in the design part of the PPDIOO
b design the solution
e validate the design
a review the cost.
BCD
Match infrastructure with the description.
i identity is AAA NAC D
ii mobility is access from arremote location A
iii Storage is storage of critical data e
iv compute is improved computational resources.
v security is secure communications.
vi voice is unified messaging.
A company location is used for a test
that is a PILOT b
An isolated location is used for a test.
That is a Prototype A
NBAR netflow are
Network analysis tools B
Monitoring Cisco works and Whatsup are.
Network audit tools A
Which are technical constraints.
existing wiring A
existing bandwidth B
Which are technical goals.
Improve the LAN C
add redundancy D
Which are organizational goals.
improve customer support A
Increase competitiveness C
Reduce operational cost E
Which are organizational constraints.
BDF
What components are in the design document.
ip scheme A
implent plan B
design requirements D
selected routing E
Match each document with the description.
i. introduction goals d
ii design requriements organizational requirements c
iii existing network current diagram b
iv design new logical topology f
v proof of concept pilot e
vi implementation plan detailed steps A
vii appendix supporting information g
Network health
is based on stats from the network c
Network audit 75% for a wan link
increase the bandwidth C
What information in a network audit report.
A device list
B IOS versions
C router models
D interface speeds
E network utliziation.
Which three steps help characterize the network
BCD
Traffic analysis
audit
Collect info
Which command shows CPU
show process CPU b
What can be obtined using the traffic analyzer.
Average bit rate. e
Which commands provide information about apps protocols flows.
show ip interface b
show ip cache flow c
show ip nbar d
what is used to create the documetnation of the current network
A show commands
b audit
c audit
d existing documentation
Sequence of top down is the
application presetnation session transport network datalink phyiscal
Which are potential scopes. ???
29
dbca
30
cd
31
abcd
32
b pilot
33 which three are in the design
b design requirements
a design details
e implementation plan.
Have some free time. So I'll just pass it.
Foundation.
PPDIOO
Prepare
Plan
Design
Implement
Operate
optimize
So far so good.
The test revolves around acronyms so memorize.
Business forces that will impact your design.
ROI - Return on investment
Companies expect either savings or improved earnings due to the devices you place.
Let's cough up an example.
Let's say I have 8 switches in my rack.

To manage them I need to connect using telnet/console to the switch and give it some commands.
Let's say I need to upgrade them. Then I would need to spend 20 minutes * 8 = 160 minutes
on an upgrade.
Let's say I want to troubleshoot the switches, then I would need 8* more screens and command typing to get the issue resolved.
You can calculate the cost of IT engineer as $50 an hour and start adding it up.
now to save money in the above example. I can convince management to purchase a
Cisco 6513 chassis.

Now, I only need to upgrade one supervisor and troubleshooting becomes easier.
So I am saving money.
The ROI is calculated by measuring how long would it take to recover the investment I just made
on the chassis.
Another way to look at ROI is by looking at the benefits of an upgrade.
Let's say the users spend 5 minutes every day till the Outlook syncs and another 5 minutes
a day wasting time waiting for files to get copied.
10 minutes * $6 an hour * 600 employees = $600 dollars of wasted time staring at the screen.
Now if I upgrade them to 1000 instead of 10/100 then they will spend 5 minutes waiting.
So 5 minutes * $6 an hour * 600 employees = $300
So if I upgrade them to 1000 Mbps switches and network cards I will be saving $300.
So 20 switches * $10000 each = $200000
Now your ROI break point or the point at which you start making money on the upgrade is
$20000/$300 = 660 days
So if I invest in upgrading the switches the company within 2 years will have made back the cost
and will be making money on the investment.
A good salesperson will easily be able to demonstrate the value and not just say
we need 1 GigE switches (1000Mbps) because they are pretty or fast.
{good salespeople are hard to come by}
Regulations
Because of companies like Enron and crackers. There are new regulations in the market.
HIPAA Health Insurance Portability Accountability Act. -
You me and everybody has a record of their visit at the Doctors, well I might have an erection problem.
Now I wouldn't want it to be published on the web when you google saar that I appear as having that.
So in order to protect the confidentiality of my medical information and transactions.
HIPAA came along with guidelines, so the Dr. needs a safe system. When he connects to my insurance
he needs to have a secure VPN. When they store my data their Database needs to be secure. etc
The second example is Visa and banks. If I can hack into a computer at a retailer that does Visa transactions
I can copy the numbers and Secure codes in the back and then go shopping!!!!!
So for that you have the PCI DSS Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard.
So now my Amazon shopping is secure and I can safely swipe my card.
The third good example is Sarbannes-Oxley. This gem was passed following Enron collapsing
without anyone having seen even a hint. It talks about auditing and how you should "measure"
kpms key performance indicators in IT.
So for us it means we have to monitor the network at Amazon, because if it collapses then the
stock goes down the toilet. So now business must track and publish KPMs so their stock owners
can asses the health of the company.
All in all, when you are selling. You can throw those around in order to get the client to be MORE secure
Competitiveness
So let's say I have a warehouse with dolls. Now my competitor just built an ecommerce site.
So now he has an advantage. To match him I must build one.
Let's say he is using two internet providers so when a storm hits I am out of business and he is running
around stealing my clients.
So now I need a more powerful router.
These three are the Business Drivers according to CCDA.
Technological Drivers
At the same time there are simple Technological drivers.
Removal of Borders
Back when I started in IT if you worked for an ISP you got a free Frame relay for home.
(this was in Dial up days). So I could work from home to solve issues.
Today with the Iphones, wireless, laptops etc. People want to work from everywhere. On the road
at the airport, at home when sick, etc. So there are no more borders. You need to give them more and more
access.
To address this you will add VPNs, remote access, tunnels etc
Virtualization
Most servers in the enterprise are no longer stand alone. Companies placed them in Virtual Servers which run on top of a Hypervisor. Vmware is one example. The Hypervisor will have 50 VMs running on it.
This leads to a very high utilization rate of the resources and a lot of flexibility.
In order to address this you will probably have to upgrade the network because storage traffic takes
a lot of resources and requires low latency.
Growth Of Applications
so yeah, back when I was a kid 1 channel was all we had on TV. Then two , 20 and now you have
800 channels, streaming VOD etc. All of this requires more and more powerful servers and networks to handle it. The programs over time also become more complex.
If before I was happy word typed a letter. Now I want graphics and links and Visios embedded etc.
So more more more horsepower from the PC and the network.
So
Business drivers are usually driven by business people.
technological ones will be driven by IT asking for resources.
IT optimization can be divided into three type.
Datacenter - ie servers, infrastructure
Network - LAN and WAN
Applications - upgrade the software on them and the application.
Each one has their own people.
Datacenter would be Dell, IBM, HP inclined people.
Network - would be CCIE's Juniper etc.
Applications - are usually programmers and software people.
You can no longer master all three unless you are in very SMB .
Cisco has created a FrameWork.
A framework is a patch of ideas or guidelines to help you talk the same lingo to other people
in the field. Which is very important. I might be peddling eggplants and the other guy is british so he is talking about Aubergines. So in the end we fail to make Baba Ganush .
As you can see there are areas
where they will intersect.
Cisco Borderless
anywhere, anytime,anything,anyone
lot's of A's
So from anywhere you go(abroad) , at anytime you want (late), anything you want (like outlook), anyone (let's say my business partners)
It also needs to be secure (VPN) , reliable (high Availiability, clusters) , seamless (one login)
It will be made from 4 Blocks.
Policy and Control - You can apply policies anywhere, if you are at home or you just came to the office
Network Services - these are services for the network, like control or energywise
User Services - like mobility , performance (acceleration), Security (vpn)
Connection management - manage the connection security everywhere.
Collaboration
Alright we got a nice network but money is made as a team effort. I need to talk to sales, they need to
talk to shipping, shipping to fed ex.
For all of this to happen you need collaboration software.
Communication and collaboration applications - telepresence (video conferencing), Email, etc
Collaboration Services - these are services for the layer above for example PRESENCE
so I know if the user is online, then I can chat him
Infrastructure - this layer provides you with the tools for the two above.
It includes virtualization , storage, network
Datacenter
Cisco builds on the Datacenter 3.0
It's a comprehensive Cisco solution to help with this.

they basically have entered the Hardware for the Datacenter market and the networking of it.
The benefits from the
Framework
are
Functionality - they support the requirements.
Scalability - they allow room for growth
Availability - reliable and anywhere anytime.
Some more examples are.
Performance - less latency, more bandwith,
Manageability - easier to use , easier to detect faults.
Efficiency - the cost is reasonable
The architecture is roughly.
Switches/ servers (nuts and bolts)
They are all easier to control with the cisco UNIFIED fabric,network and computing. (software)
They result in better energy , workload, efficiency
and allow you to virtualize, cloud, automate and consolidate (high level)
Alright,
back to PPDIOO
Prepare
Plan
Design
Implement
operate
optimize.
Keep drilling that cycle that Cisco recommends.
The benefits of using it are.
Lowers the Total Cost of Ownership TCO by validating and planning
Increases availability by producing a sound design and validating it.
Improve the business agility by establishing business requirements and strategic technologies.
Speed access to applications - byimproving performance,availability reliability, scalability.
Actions that lower the total cost of ownership are.
identify and validate the technology - for example identify you need a chassis and test it
plan for infrastructure changes and growth - for example the chassis will be flexible on the line cards you add
Develop a sound design with business goals - a business goal can be more reliability which the
chassis will handle with Dual Supervisors.
Accelerate the implementation - less downtime due to solid implementation.
Improve the network and management - make it easier to manage.
reduce operating cost by improving the process - for example the chassis allows for easier management
Actions that increase availability are.
Asses the network - so it can withstand the traffic.
Specify the hardware and software and keep it current by updating the software (smartnet)
Produce a sound design - so it won't collapse
stage and test -- to make sure it works in your network and not just on the datasheet
Improve staff skills - so they will know what to do.
Proactively monitor the network - so you can predict growth and problems
Proactively manage the security - so you can block breaches and remediate breaks.
Actions that improve business agility
establish the business requirements.
ready the sites and the people
Integreate the technical aspect and align it with the business requirement.
expertly install
continually monitor it
Actions that accelerate the application and services
assess the network
improve the service delivery
improve availability
Manage and resolve problems and keep everything up to date.
As you can see this is a cycle.
Prepare
This phase is where you come up with the Business case.
The business case creates a justification for the expenditure of time and money.
Technologies that support the architecture you are planning will be considered.
Plan Phase.
Here you drill down and identify user needs and goals.
You will also assess the network and see if there is a GAP against best practices and documentation.
You will develop a PROJECT plan with the resources milestones and identify the resources
for the design phase.
Design Phase.
Based on the previous data you gathered and in allignment with the business goals
you will produce a detailed design.
The design will include the Visio diagrams and equipment list.
You will also make the project plan more granular.
Once the design is approved you move to implement it.
Impelentation phase.
New equipment is set up and configured.
Changes should be brought up in change meetings to minimize downtime
Each step should have.
1. description
2. Detailed implementation
3. time to implement
4. guidelines for rolling it back in case of failure.
5. changes must be tested to validate them.
Operate phase.
At this stage you operate the equipment.
Day to day work along with accumulating data for the next stage.
Optimize stage.
At this phase you use the data from operations to see if there is room for improvement.
Also you analyze any problems.
If there is room for change.
You can start the Prepare phase and place a business case for improvement or change
which will start the cycle again.
Since this is CCDA concentrate on the first three stages.
Step 1 Prepare - identify the client requirements as far as business and give a conceptual architecture.
for example : the client is complaining about latency. So conceptually we will look at Nexus 3000
Step 2 Plan - Come up with an assesment of what he has now and the weakpoints or adjustments.
come up with a project plan to move ahead.
Step 3 Design - come up with a detailed design plan and granular project plan
When you run the prepare.
Talk to business managers and to department heads and users to see WHAT they need
business wise .
You can use the
1. Identify the applications and services. -example exchange and outlook.
2. Define the organizational goals example we want outlook to be more responsive and robust
3. define organizational constraints example we have a low budget.
4. Define the technical goals example improve latency by 30%
5. Define technical constraints example the switches are eos and outdated.
You can help yourself by using a template.
now you will have all of the applications identified and the requirements of them.
So the organization wants us to improve the performance of outlook.
now you can identify organizational constraints
For example. The IT goes on holiday for a month.
We lack a high budget - so maybe we get pre-owned.
HIPAA mandates we use IPSEC security for the VPN (which slows down a VPN)
Technological goals is where you can set the deliverables , like reduce latency by %
technological constraints can be cabling issues. Sites. legacy equipment
So far so good.
This is all in the Prepare.
Characterizing the network.
Simply go and ask for any current documentation.
Then validate the documentation to see it is relevant and add more detail.
After that you can run analysis tools to gather data on traffic and protcols.
Site, lan , wan ,power, cabling, rooms
Use existing documentation
Existing tools
or buy new tools.
Cisco Works can give you hardware and software.
make it pretty granular.
Device type - model -software on it - configurations - data from tools - speeds -CPU/mem - WAN data
This can be quite extensive however it can help for building a better design.
Tools
Cisco Works - maps the network and collects the hardware and software
Netflow - gives you data on the traffic.
NBAR - analyzes the application flows.
Third party tools -
Additional tools can be used for example for wireless.
Airmagnet - can analyze interference.
Commands for Cisco.
show tech-support gives you a detailed output
show process CPU - gives you a CPU reading
show version - will show you the IOS you are running.
show process memory - gives you the memory usage.
show log - will give you errors on the log
show interface - will give you stats on the interface.
show policy-map interface will show you policy maps on it.
show running-config will give you the configuration so you can assess the current network design.
show ip cache-flow
will give you the netflow output.
CNS Cisco netflow collector engine collects netflows from devices.
Checklist for best practices
Nework LAN should use switches and not hubs.
no WAN link is saturated anything above 70% is a red flag.
Response times should be less than 100ms or 2ms in the LAN.
Segments should not have more than 20% broadcast /multicast
Ethernet should not have more than 0.1 percent collisions (high utilization leads to collisions)
CPU of more than 75% for more than 5 minutes is a red flag.
output queue drops should not exceed 100 for an hour
Input queue drops should not exceed 50 for an hour
buffer missed 25 per hour
ignored should not exceed 10
QoS should be configured for VOIP or other sensitive traffic.
Steps were
Documentation
Audit of the network - cisco works
Traffic analysis - CNS analyze netflow.
Designing the network.
In order to validate the design you can use a
Prototype - which is a separate network test. (in a lab)
Pilot - a test run on a live network (for example only in the IT department)
Design from the TOP of the model down.
Application needs
then only the transport network and data link physical
Top - Down is more time consuming however more reliable.
Bottom - up relies on experience but can be prone to error.
Design Document -
This document details the business requirement + conceptual design.
The current network and gaps.
Then the design plan, configuration and testing.
1. Introduction - sometimes called the executive summary.
2. Design requirement - that are the business ones
3. existing network - add diagrams and data accumulated from the audit.
4. Design - and why it solves the requirements and addresses the current
5. Validation - data on the testing that was done. also called Proof of Concept.
6. Impelentation plan - for the Staff on how to impelement the design.
7. appendixes with all the detailed data gathered.
Before you move on you need to create a detailed implementation plan.
1. Step
2. reference to the design document
3. detailed implementation of the step.
4. detailed rollback.
5. estimated time to complete.
Q&A
list the PPDIOO
Prepare
plan
design
implement
operate
optimize
which business forces affect the design.
ROI
REgulations
business competitivenes.
efg
Which step is critical in identifying the organizational goals.
Identify customer requriements a
What needs to be obtained prior to designing the network.
Organizational goals
technical constraints
existing applications
bce
Match each PPDIOO with
i implement installation and config
ii optimize proactive management
iii design provides HA design
iv prepare Gap analysis
v operate day to day
vi plan Establish requirements.
Which borderless architecture provides mobility.
User services provide mobility
Which are three steps in the design part of the PPDIOO
b design the solution
e validate the design
a review the cost.
BCD
Match infrastructure with the description.
i identity is AAA NAC D
ii mobility is access from arremote location A
iii Storage is storage of critical data e
iv compute is improved computational resources.
v security is secure communications.
vi voice is unified messaging.
A company location is used for a test
that is a PILOT b
An isolated location is used for a test.
That is a Prototype A
NBAR netflow are
Network analysis tools B
Monitoring Cisco works and Whatsup are.
Network audit tools A
Which are technical constraints.
existing wiring A
existing bandwidth B
Which are technical goals.
Improve the LAN C
add redundancy D
Which are organizational goals.
improve customer support A
Increase competitiveness C
Reduce operational cost E
Which are organizational constraints.
BDF
What components are in the design document.
ip scheme A
implent plan B
design requirements D
selected routing E
Match each document with the description.
i. introduction goals d
ii design requriements organizational requirements c
iii existing network current diagram b
iv design new logical topology f
v proof of concept pilot e
vi implementation plan detailed steps A
vii appendix supporting information g
Network health
is based on stats from the network c
Network audit 75% for a wan link
increase the bandwidth C
What information in a network audit report.
A device list
B IOS versions
C router models
D interface speeds
E network utliziation.
Which three steps help characterize the network
BCD
Traffic analysis
audit
Collect info
Which command shows CPU
show process CPU b
What can be obtined using the traffic analyzer.
Average bit rate. e
Which commands provide information about apps protocols flows.
show ip interface b
show ip cache flow c
show ip nbar d
what is used to create the documetnation of the current network
A show commands
b audit
c audit
d existing documentation
Sequence of top down is the
application presetnation session transport network datalink phyiscal
Which are potential scopes. ???
29
dbca
30
cd
31
abcd
32
b pilot
33 which three are in the design
b design requirements
a design details
e implementation plan.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)




































